K
Kelly Koder
Guest
Visit [CCO] Medical Coding for more articles about [CCO] Medical Coding - Learn It - Get Certified - Stay Certified.
What do you mean by medical auditing?
Medical auditing is a process used by health professionals to assess, evaluate and improve care of patients in a systematic way. Audit measures current practice against a defined (desired) standard. It forms part of clinical governance, which aims to safeguard a high quality of clinical care for patients.
Key features of audit are:
Source: http://patient.info/doctor/audit-and-audit-cycle
To cut it short, it’s just double-checking and making sure what is being coded is accurate and you have all these computer programs and audit tools you can use during the process.
What does a Certified Professional Medical Auditor (CPMA) do?
The goals of an audit are to provide efficient and better delivery of care and to improve the financial health of your medical provider. Medical record audits specifically target and evaluate procedural and diagnosis code selection as determined by physician documentation. Once areas of weakness are revealed through an audit, you can present the audit findings and identify opportunities for training in your health care organization. Source: https://www.aapc.com/medical-auditing/medical-auditing.aspx
They will also review and audit medical coding data. Corrections to this data will also be made by the medical coding auditor. When medical coding assignments seem wrong and mistakes seem to be repeated, the auditor may have to report this to management, or he or she may have to make inquiries to the department that had created the documentation. Feedback is also given on performance results. The auditor may also be required to provide training and education.
In a nutshell, a medical coding auditor:
Source: http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Medical_Coding_Auditor/Salary
Medical Auditing Career: What Are The Opportunites for Medical Auditors — VIDEO
Medical Auditing Salary
According to PayScale, most medical coding auditors in the United States are women. The median pay for people in this role is approximately $54K annually. Pay generally varies between $34K and $74K per year. Residence is the biggest factor affecting pay for this group, followed by years of experience. Most report receiving medical coverage from their employers and a strong majority collect dental insurance. The majority of Medical Coding Auditors claim high levels of job satisfaction. Source: http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Medical_Coding_Auditor/Salary
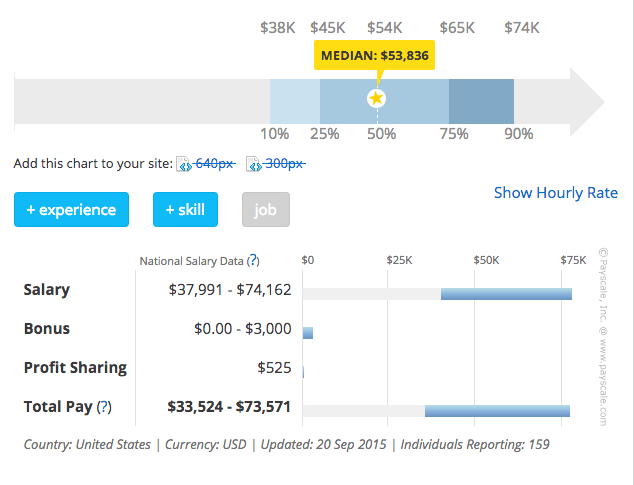
The data for this synopsis comes from respondents who took the PayScale salary survey.
Medical Auditing Certification & Training
There are numerous routes to a career in medical auditing. The minimum requirement for the job is a post-secondary certificate. Associate degree options are also available. In most cases, a certificate can take up to one year to complete and an associate’s degree requires two years. However, most employers want to hire someone who has experience in the medical field in addition to the certificate or associate’s degree. They might also seek out those who have earned a bachelor’s degree in a medical field, such as health science, medical records technology, nursing, health service administration or business with an emphasis on medical laws and ethics.
Medical auditing training can be completed online. Most programs focus strongly on topics that lend themselves well to online education, such as healthcare compliance practice, communications and accounting. Since no hands-on element is required in these programs, students can choose an online-only degree or certificate program that can be taken at their own pace. This allows students to juggle work and family obligations while earning their degree.
Another advantage of online education is a compressed time-frame in which courses are often completed. Certificates can be earned in as little as six months, and associate degrees in as little as 15 months, depending upon the school, institution, or organization and the availability of the student. Those who choose to take online courses also have the opportunity to hone their computer and research skills, which are both necessary for compliance and auditing work. Source: http://www.medbillingcodingonline.org/medical-compliance-and-auditing/
If you are interested in taking your medical coding career to the next level and prove your worth as a CPMA, click on the link below to learn more about medical auditing — courses, certification, and training!
Related Medical Auditing Posts:

The post Medical Auditing — A Growing Career Path for Medical Coders appeared first on [CCO] Medical Coding.
Continue reading...
What do you mean by medical auditing?
Medical auditing is a process used by health professionals to assess, evaluate and improve care of patients in a systematic way. Audit measures current practice against a defined (desired) standard. It forms part of clinical governance, which aims to safeguard a high quality of clinical care for patients.
Key features of audit are:
- Audit asks the question: ‘Are we actually doing what we believe is the right thing, and in the right way?’ (unlike research, which asks ‘What should we be doing?’).
- Audit can be used to evaluate various aspects of patient care:
- Structure of care – eg, the availability of a smoking cessation clinic in a locality.
- Process of care – eg, waiting times for an appointment at the smoking cessation clinic.
- The outcome of care – eg, the number of smokers who quit smoking for one year.
- Audit should be transparent and non-judgemental. The aim is to find out how the present provision compares with the desired standard. This information can then be used to plan improvements in the service. It is not intended to cause confrontation or blame.
Source: http://patient.info/doctor/audit-and-audit-cycle
To cut it short, it’s just double-checking and making sure what is being coded is accurate and you have all these computer programs and audit tools you can use during the process.
What does a Certified Professional Medical Auditor (CPMA) do?
The goals of an audit are to provide efficient and better delivery of care and to improve the financial health of your medical provider. Medical record audits specifically target and evaluate procedural and diagnosis code selection as determined by physician documentation. Once areas of weakness are revealed through an audit, you can present the audit findings and identify opportunities for training in your health care organization. Source: https://www.aapc.com/medical-auditing/medical-auditing.aspx
They will also review and audit medical coding data. Corrections to this data will also be made by the medical coding auditor. When medical coding assignments seem wrong and mistakes seem to be repeated, the auditor may have to report this to management, or he or she may have to make inquiries to the department that had created the documentation. Feedback is also given on performance results. The auditor may also be required to provide training and education.
In a nutshell, a medical coding auditor:
- Contribute to the development of codes for patient billing.
- Conduct analyses to evaluate the accuracy and efficiency of coding practices.
- Review the work of coding clerks to verify accuracy of coding and that patients are billed correctly.
Source: http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Medical_Coding_Auditor/Salary
Medical Auditing Career: What Are The Opportunites for Medical Auditors — VIDEO
Medical Auditing Salary
According to PayScale, most medical coding auditors in the United States are women. The median pay for people in this role is approximately $54K annually. Pay generally varies between $34K and $74K per year. Residence is the biggest factor affecting pay for this group, followed by years of experience. Most report receiving medical coverage from their employers and a strong majority collect dental insurance. The majority of Medical Coding Auditors claim high levels of job satisfaction. Source: http://www.payscale.com/research/US/Job=Medical_Coding_Auditor/Salary

The data for this synopsis comes from respondents who took the PayScale salary survey.
Medical Auditing Certification & Training
There are numerous routes to a career in medical auditing. The minimum requirement for the job is a post-secondary certificate. Associate degree options are also available. In most cases, a certificate can take up to one year to complete and an associate’s degree requires two years. However, most employers want to hire someone who has experience in the medical field in addition to the certificate or associate’s degree. They might also seek out those who have earned a bachelor’s degree in a medical field, such as health science, medical records technology, nursing, health service administration or business with an emphasis on medical laws and ethics.
Medical auditing training can be completed online. Most programs focus strongly on topics that lend themselves well to online education, such as healthcare compliance practice, communications and accounting. Since no hands-on element is required in these programs, students can choose an online-only degree or certificate program that can be taken at their own pace. This allows students to juggle work and family obligations while earning their degree.
Another advantage of online education is a compressed time-frame in which courses are often completed. Certificates can be earned in as little as six months, and associate degrees in as little as 15 months, depending upon the school, institution, or organization and the availability of the student. Those who choose to take online courses also have the opportunity to hone their computer and research skills, which are both necessary for compliance and auditing work. Source: http://www.medbillingcodingonline.org/medical-compliance-and-auditing/
If you are interested in taking your medical coding career to the next level and prove your worth as a CPMA, click on the link below to learn more about medical auditing — courses, certification, and training!
Related Medical Auditing Posts:
- Medical Auditing Career — Should a New Coder Take a Medical Auditing Course?
- Medical Auditing Career | What are the Opportunities for Medical Auditors? – Video
- Medical Auditing Courses | What Kind of Person Signs up for a Medical Auditing Course? – Video

The post Medical Auditing — A Growing Career Path for Medical Coders appeared first on [CCO] Medical Coding.
Continue reading...
